We know that wind pressure is the pressure of the wind on a plane perpendicular to the direction of the air flow. According to the wind-pressure relationship derived from the Bernoulli equation, the dynamic pressure of the wind is wp = 0.5 · ro · v2 where wp is the wind pressure [kN / m2], ro is the air density [kg / m3] and v is the wind speed [ m / s].
Since the relationship between air density (ro) and severity (r) is r = ro · g, there is ro = r / g. Use this relationship in (1) to get
wp = 0.5 · r · v2 / g (2)
This formula is the standard wind pressure formula. Under standard conditions (air pressure of 1013 hPa, temperature of 15 ° C), the air has a severe r = 0.01225 [kN / m3]. Gravitational acceleration at a latitude of 45 ° g = 9.8 [m / s2], we get wp = v2 / 1600 (3)
This formula is used to estimate wind pressure wind speed of the general formula. It should be noted that the severity of air and acceleration of gravity vary with latitude and altitude. In general, r / g is less on the plateau than in the plains, which means that the same wind speed at the same temperature produces less pressure on the plateau than in the plains.
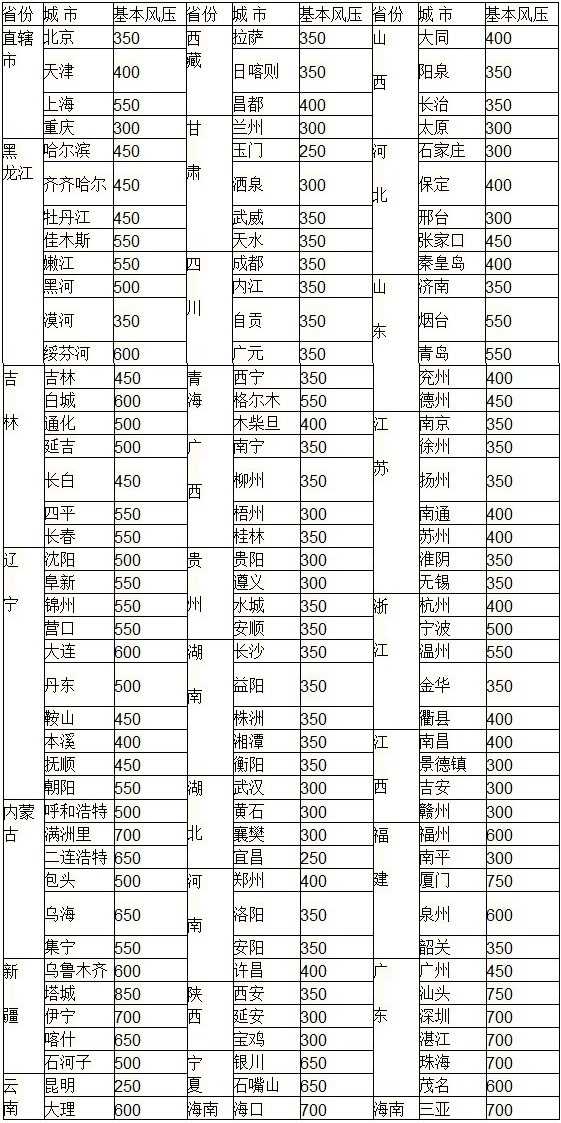
Wind pressure reference table in some parts of China: